Androgenetic Alopecia: Causes & Best Hair Transplant Options
For many, even gradual hair loss can affect their self-esteem. Androgenetic alopecia causes thinning hair and baldness in men and women around the world. This is a genetic condition with some hormonal triggers, especially dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Although most commonly associated with male pattern baldness, women also suffer from visible hair loss from this condition. Fortunately, thanks to new treatment options, we can slow down or, in some cases, reverse hair loss! The article discusses the reasons, signs, and some of the best treatments for androgenetic alopecia.
Understanding Androgenetic Alopecia
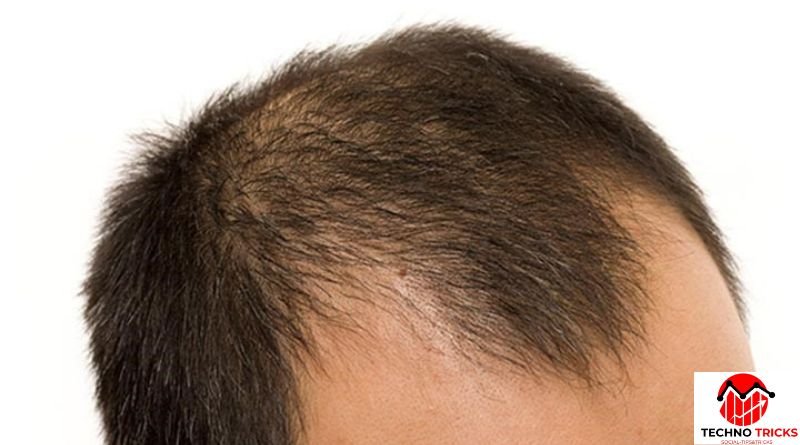
Androgenetic alopecia is a slow kind of hair loss with a predefined sample. It results from a confluence of hormones and genes. While women normally experience diffuse thinning along the portion line, men frequently find their hairline recedes from the temple and crown. If neglected, the disorder gets worse with time and, in severe cases, results in irreversible baldness. Studies reveal that DHT, a testosterone side effect, is vital in reducing hair follicles, slowing their growth cycle, and finally bringing them to stop producing. Although androgenetic alopecia cannot be totally stopped, early management helps to decrease its development and restore hair density.
Symptoms and Progression of Androgenetic Alopecia
The first noticeable symptom of androgenetic alopecia is gradual hair thinning. Men often see a receding hairline and bald patches at the crown, which can eventually merge into widespread baldness. Women, on the other hand, experience a more even thinning of hair, with a widened part and reduced hair volume. The condition progresses in stages, classified using the Norwood-Hamilton scale for men and the Ludwig scale for women. Some individuals may also experience increased hair shedding, indicating weakened follicles. Since early intervention yields better results, those noticing signs of hair loss should consult a specialist to explore treatment options before the condition advances significantly.
What Causes Androgenetic Alopecia?
Androgenetic alopecia is mostly caused by inherited DHT sensitivity, which weakens and miniaturises hair follicles over time. Those having a family history of baldness are more prone to get this disorder. Apart from genes, elements including hormone fluctuations, ageing, and lifestyle decisions can lead to hair loss. Poor diet, ongoing stress, and too frequent chemical hair treatment use could hasten the process. Furthermore, aggravating hair thinning in women are medical illnesses such as thyroid problems and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Although genes cannot be altered, controlling lifestyle choices and getting medical treatment can help to slow down the development of androgenetic alopecia.
Can You Prevent Hair Loss?
Although total prevention of androgenetic alopecia is not feasible, various steps can slow down its start and reduce its effects. Keeping a nutrient-dense diet, especially one heavy in iron, biotin, and vitamin D, can help to encourage good hair development. Massages of the scalp gently increase blood flow, therefore strengthening hair follicles. Also beneficial is lowering stress with mindfulness practices, including yoga and meditation. Steer clear of too-tight hairstyles, strong chemicals, and too much heat styling to avoid needless hair damage. Seeking professional assistance at the initial stages of hair loss also enables people to investigate preventative treatments, including oral drugs and topical remedies, before major thinning takes place.
Best Treatment Options
And there are now tried and examined remedies to be had to offer a satisfactory level of hair permanence for the ones affected. Among the most amazing options are FDA-permitted tablets, such as minoxidil, which enables the stimulation of hair follicles, and finasteride, which minimizes the manufacturing of DHT. Long-time period solutions for hair recuperation are to be had from hair transplants observed via Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) and Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT). Novel remedies consisting of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections and occasional-level laser therapy (LLLT) look powerful in stimulating hair regrowth. Hair loss may come to be plain with advances in stem mobile therapy and regenerative medicine. Treatment options should be based on the degree of hair loss and private choice.
Choosing the Right Hair Transplant Option
A hair transplant is a reliable therapy for patients suffering from severe hair loss. Two most often used methods are FUE and FUT. Individual follicles are removed and placed into thinning regions in a FUE operation, therefore reducing scarring and hastening healing. FUT is appropriate for those needing more extensive grafts since it entails removing a strip of scalp with healthy hair follicles and transplanting it into bald areas. Robotic hair transplants, which guarantee natural-looking outcomes and improve accuracy, have also lately been available. The best course of action depending on hair loss degree, scalp condition, and desired outcomes depends on consulting a specialist.
Conclusion
Hair loss can have an effect on one’s self-esteem and confidence, but with the correct treatment plan, people can restore a fuller, healthier head of hair. Key to good therapy is early intervention, which is made possible by knowing the causes and symptoms of androgenetic alopecia. There are several answers, whether from drugs, cutting-edge treatments, or a hair transplant. Choosing the correct strategy and consulting a specialist will enable people to get the greatest potential outcomes.
May Also Read: thetechnotricks